- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Voltage applied to a series circuit is equal to the sum of the individual voltage drops. In a series circuit the voltage drop across each resistor will be directly proportional to the size of the resistor.

Physics Tutorial Parallel Circuits

Resistors In Series And Parallel Physics

Physics Tutorial Parallel Circuits
Multiply the current by the total resistance to get the voltage drop according to ohms law v ir.

Voltage drop for resistors in series. Resistors in series carry the same current but the voltage drop across them is not the same as their individual resistance values will create different voltage drops across each resistor as determined by ohms law v ir. Once you have the current calculate voltage for the individual resistors by multiplying the current by the resistance. This equals the voltage drop across the entire parallel circuit and each resistor in the parallel circuit.
Then series circuits are voltage dividers. For this example the voltage drop is given v 5 a x 157 w 757 v. Since there is 05 amps through each resistor the voltage drop across the first 5 ohm resistor is 25 volts and the voltage drop across the second 15 ohm resistor is 75 volts.
The voltage drop across a resistor in a series circuit is directly proportional to the size of the resistor. Notice the voltage drops across each resistor and how the sum of the voltage drops 15 5 25 is equal to the battery supply voltage. For the 2 ohm resistor the voltage would be 12 times 2 or 24 volts.
The voltage drop in each of the series resistors is equal to the current though the loop multiplied by the resistor value. This is the third principle of series circuits. If the circuit is broken at any point no current will flow.
For example in a series circuit with 3 resistors of 2 3 and 5 ohms and a voltage of 12 volts the current would be 12 divided by 10 or 12 amperes. For a dc circuit with constant voltage source v t and resistors in series the voltage drop v i in resistor r i is given by the formula. In a parallel circuit the voltage drop across each resistor will be the same as the power source.
Ohms law is conserved because the value of the current flowing through each resistor is different. The supply voltage in a series circuit is equal to the sum of the individual voltage drops.

Series And Parallel Resistances Pg 51 Objectives Calculate

Eet 1150 Unit 5 Ohm S Law

Resistors In Series And Parallel College Physics
Why Is The Voltage Divided In A Series Connection Quora
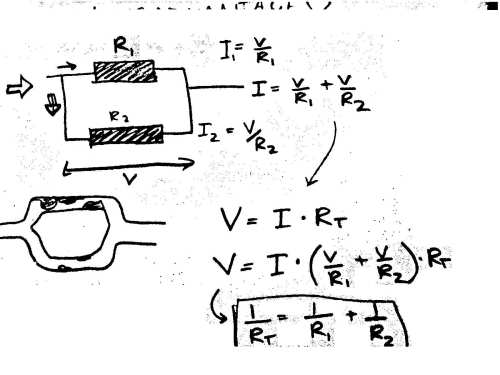
Background Science Engineering Concepts Series And Parallel

Potential Difference And Resistor Voltage Division

Voltage Drop

Voltmeter Design

Led Resistor Calculator

Physics Tutorial Parallel Circuits

Solved A Suppose You Have A Simple Circuit With Two Resi

Zener Diode Series Resistor Calculator
Comments
Post a Comment